Has starting your own business always been your dream? Then you must take the step and also learn about some significant terms for long-term success. Turnover and revenue come in handy when measuring performance.
Although these terms often describe similar concepts, they differ in meaning and function. Many business owners and finance managers confuse turnover vs revenue and make mistakes when making financial plans.
We see how important this is, so we have explained the differences between turnover and revenue and how to calculate them. Stay with us until the end to get a clear understanding of the differences between revenue and turnover.
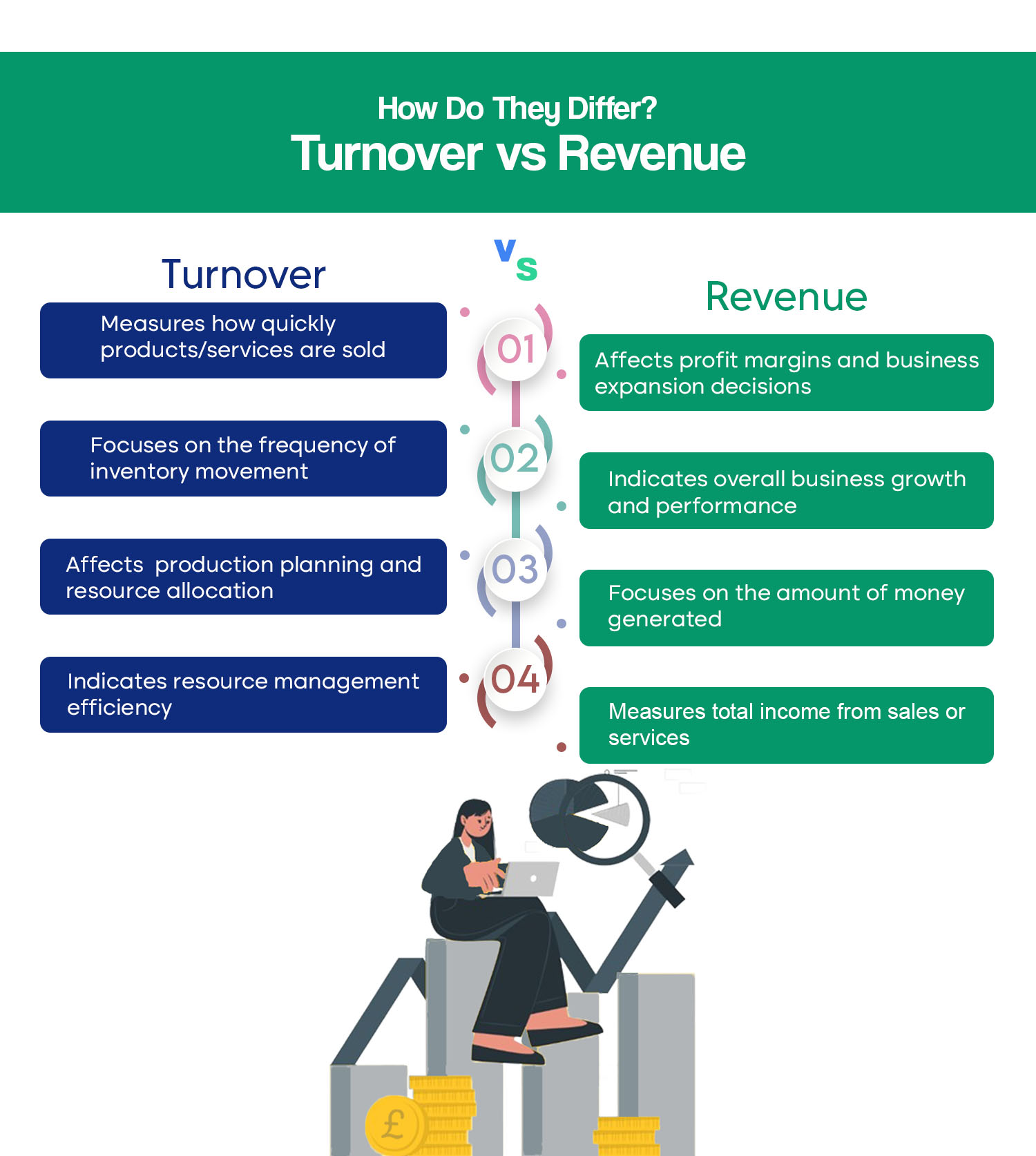
Table of Contents
Definition of Turnover vs Revenue
Turnover means how many times your business sells or burns through its assets. A high turnover rate generally indicates that your business is doing well, selling items rapidly and refreshing the stock regularly.
For retail and manufacturing companies maintaining a high turnover rate is a necessity. However revenue means the total income your company earns after selling goods or services for a fixed price to its customers. It’s also called the sales your company generates or income but it differs from profit.
Profit is what you get after subtracting all costs from your generated yearly or monthly revenue, such as salaries and rent. Although revenue shows the total amount you earn, profit shows how much your company keeps.
Grow Your Practice with Confidence
Differences in Turnover vs Revenue
At every business networking event, the discussion about revenue and turnover takes center stage. Many business owners ask several questions for clarity, but what’s the real difference? While you’ll notice that both go hand in hand, turnover and revenue are different.
Here are some major differences between turnover and revenue.
| Turnover | Revenue |
| Measures how quickly products/services are sold | Measures total income from sales or services |
| Focuses on the frequency of inventory movement | Focuses on the amount of money generated |
| Indicates resource management efficiency | Indicates overall business growth and performance |
| Affects production planning and resource allocation | Affects profit margins and business expansion decisions |
Calculating Turnover
You’ll come across three types of turnover: inventory, asset, and receivable, so let’s learn how to calculate each type of turnover one by one:
- Select an accounting period such as annually, quarterly, or monthly and then calculate your inventory turnover. Then, you can calculate your average inventory by adding both starting and ending values and dividing the value you get by two.
Afterward, find the cost of goods sold by adding the starting inventory to overall purchases and subtracting the ending inventory. To find your inventory ratio, divide the cost of goods sold by your average inventory.
- Calculate asset turnover, subtract returns, discounts, and allowances from gross sales to get net sales. Then, add the values for liabilities and equity to calculate total assets. Finally, divide your net sales by total assets, and the value you get is the asset turnover ratio.
- Calculate receivable turnover by selecting a period first, such as yearly, quarterly, or monthly. The next step is to calculate average receivable accounts by starting with the beginning and ending values and then dividing them by two.
Calculate net credit sales by subtracting returns and allowances from credit sales. Then, divide net credit sales by average receivables to find the receivable turnover ratio.
Example of Calculating Turnover
You own a clothing company and want to check its inventory turnover. Your inventory was valued at £400,000 at the start of the year. At the end of the year, your inventory value was £450,000 and you earned £300,000 by selling clothes.
Finding average inventory involves adding £400,000 and £450,000 and dividing it by 2 to get £425,000. The turnover ratio you’ll get is £300,000 so divide it by £425,000. You’ll get the value 0.706 which means your company sold about 70.6% of its inventory this year.
Calculating Revenue
Calculating revenue is simple. You only need to use the following two formulas, which help show the total income before any expenses are deducted.
- Revenue = number of units sold × average price per unit.
- Revenue = number of customers × average price of services.
Grow Your Practice with Confidence
Example of Calculating Revenue
A bakery sells cupcakes for £5 each, and it sold 50,000 cupcakes last year. Its yearly revenue is £250,000, which you calculate by multiplying £5 by £50,000. People returned nearly 1,000 defective cupcakes to the bakery, and the return value was £5,000. Thus, the net revenue is £245,000 because you lost £5,000 in returns.
Significance and Effects on Business
Being a business owner who aims to be successful you can’t ignore revenue or turnover. Instead you must use them to measure your businesses performance over a financial year. If you’re experiencing an increase in your revenue it means that your company is growing and targeting the right audience.
This growth allows businesses to make better decisions about expansion and investments. On the other hand, turnover rates will help you understand how efficiently you’re managing your resources.
A high turnover rate can indicate that you are using your resources effectively and need to follow the same roadmap but a low turnover rate shows that your production planning needs amendments.
Requirements for Financial Reporting
Businesses must prepare reports about financial information while following the set rules and guidelines. Following the guidelines indicate that you’re ensuring transparency and accuracy in financial statements.
Businesses must include details about both revenue and turnover in their reports. Your stakeholders will use that information to understand your company’s current financial health and performance.
Moreover, accurate reporting is important for gaining the trust of investors and lenders. Clear financial reports can lead to better decision-making and increased opportunities for growth.
Conclusion
Understanding turnover vs revenue will help you assess your company’s performance. Revenue shows how much money your business made by selling, while turnover relates to the efficiency of operations.
When you know how to calculate them and their major differences, you can make better financial decisions and come up with better techniques. To enhance your business’s financial health, regularly track both metrics. Monitoring revenue helps identify growth opportunities and customer trends.
Analyzing turnover reveals efficiency in managing resources and production levels. Always ensure accurate financial reporting to maintain transparency with stakeholders. Finally, use these metrics to set realistic business goals. An approach like this will help you improve your business approaches and guarantee long-term success.

